How can African businesses adopt a circular economy?
The circular economy offers a sustainable solution for African businesses looking to optimize their resources while limiting their environmental impact.
Discover how to integrate this innovative model into your operations.
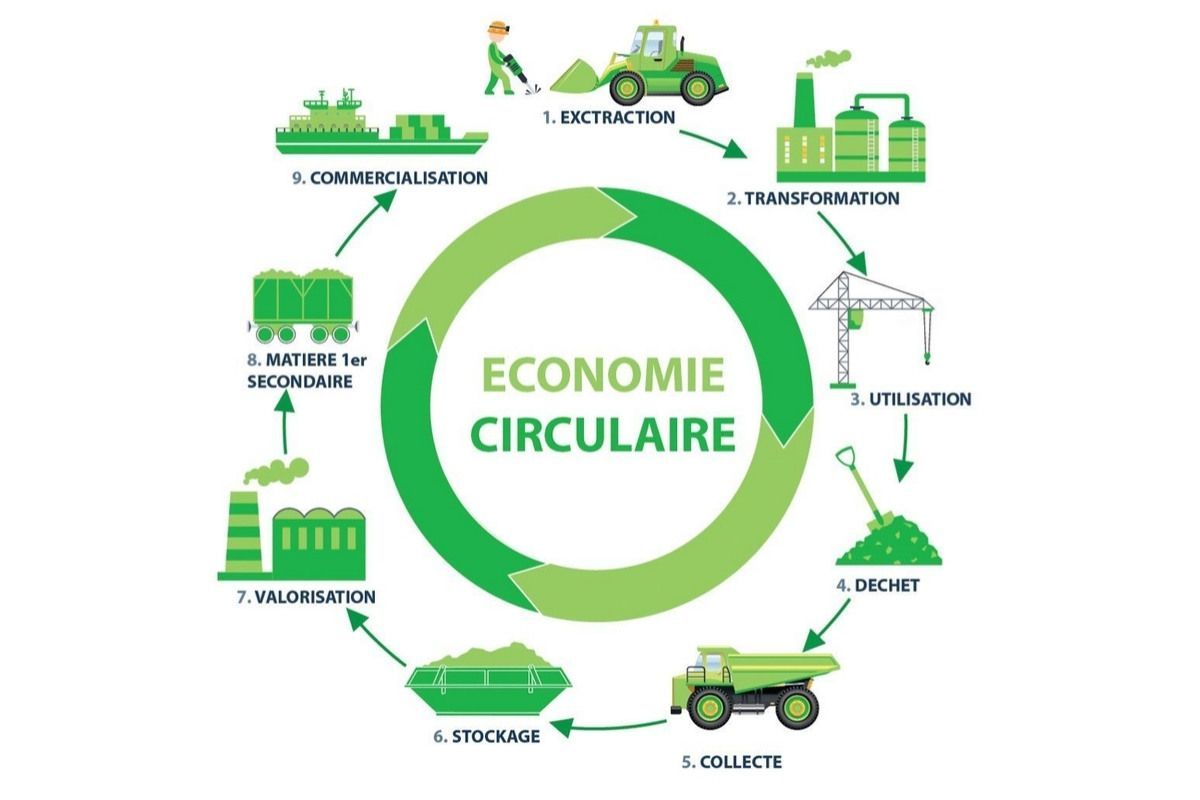
1. Understanding the Principles of the Circular Economy
The circular economy is based on three main principles:
- Waste Reduction: Reusing and recycling materials to minimize waste.
- Sustainable Design: Creating products that are easy to repair or recycle.
- Resource Optimization: Using raw materials efficiently to extend their lifecycle.
These principles are particularly well-suited to African contexts, where natural resources must be managed wisely.
2. The Benefits of the Circular Economy for African Businesses
Adopting a circular model offers numerous advantages:
- Cost Reduction: Decreasing expenses related to the purchase of new raw materials.
- Job Creation: Developing new industries focused on recycling and repair.
- Enhanced Brand Image: Positioning as a responsible and innovative market player.
- Access to New Markets: Integration into global value chains that promote sustainable practices.
3. Steps to Integrate a Circular Economy into Your Value Chain
Here are the key steps for a successful transition to a circular economy:
- Initial Assessment: Identify improvement opportunities within your current processes.
- Strategic Partnerships: Collaborate with local suppliers and recyclers.
- Eco-Design: Redesign your products to make them durable and reusable.
- Employee Training: Raise awareness among your teams about circular economy practices.
- Impact Measurement: Monitor environmental and economic performance to refine your strategies.
4. Examples of the Circular Economy in Africa
Several African businesses are standing out through their circular initiatives:
- Plastic Recycling: Start-ups are transforming plastic waste into construction materials or recycled products.
- Sustainable Agriculture: Organic waste is being used to produce natural fertilizers.
- Ethical Fashion: Clothing is being created from recycled textiles or local natural fibers.
These initiatives showcase the positive impact the circular economy can have on communities and the environment.
By adopting a circular economy, African businesses can not only help preserve natural resources but also increase their profitability and resilience in the face of economic challenges.
Start your transformation today and become a key player in sustainable development in Africa.
RISKS RELATED TO THE ATMOSPHERE
- Risk of anoxia due to oxygen levels below 19%
- Risk of asphyxiation or acute intoxication

RISK OF FIRE AND EXPLOSION
Flammable gases and chemical products combined with poor ventilation can reach their explosive range

RISK OF BURNS
From chemical products, hot water, or contact with heat networks

RISK OF FALLING FROM HEIGHTS
Related to access points

RISK OF ELECTROCUTION OR ELECTRICAL SHOCK
- Work on electrical installations
- Power supply circuits for lighting devices

RISKS RELATED TO MANUAL HANDLING
Equipment and materials

2. Training and Certification of Workers
For all work in confined spaces, GBA only employs qualified personnel.
The selection process for workers includes the following steps:
- Medical examination by our occupational health physician
- Confined space entry certification training
- Industrial risk training levels 1 and 2
- ATEX zone training
- Certification training for working at heights
- Training on the use of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) and Collective Protective Equipment (CPE)
- Training on the use of fire extinguishing equipment
- Document certifying the worker’s authorization to operate in confined spaces
3. Confined Space Entry Permit
An entry permit must be issued before starting any work. This document must include:
- A description of the task to be performed.
- The duration of the intervention.
- The necessary authorizations.
- The required safety conditions.
4. Monitoring and Control of Environmental Conditions
- Pre-entry atmospheric testing:
- Measure oxygen levels (minimum 19.5%, maximum 23.5%).
- Detect toxic gases (H₂S, CO, etc.).
- Check for the absence of explosive gases (concentration below 10% of the Lower Explosive Limit, LEL).
- Continuous monitoring during the intervention using fixed or portable gas detectors.
- Adequate ventilation to maintain a breathable environment.
5. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
- Safety helmet.
- Gloves resistant to the handled substances.
- Respirators or self-contained breathing apparatus (SCBA) in case of toxic gas risk or oxygen deficiency.
- Safety harness to facilitate rescue operations in an emergency.
- Chemical-resistant or flame-retardant clothing, if necessary.
6. Rescue Equipment and Communication System
- Rescue equipment ready for immediate use:
- Tripods or winches for rapid extraction of workers.
- First aid kit.
- Fire extinguishers appropriate to the identified risks.
- Reliable communication system:
- Radios or intercoms to maintain contact between teams inside and outside the confined space.
7. Supervision Team
- Presence of a rescue team:
- An attendant stationed outside the confined space to monitor workers inside.
- Trained attendants capable of intervening in case of emergency.
- Rescue team equipped and ready to act immediately.
8. Emergency and Rescue Plan
- Develop an emergency intervention plan:
- Rapid evacuation procedures.
- First aid management.
- Coordination with local emergency services (firefighters, ambulances).
9. Equipment Inspection
- All equipment (PPE, gas detectors, power tools, etc.) must be:
- Inspected before each use.
- Compliant with standards and in perfect working condition.
10. Regulatory Compliance
- Comply with local and international standards, such as:
- OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration).
- NFPA (National Fire Protection Association).
- ISO 45001 (Occupational Health and Safety Management System).
11. Documentation and Follow-up
- Intervention report:
- Document all steps, incidents, or observations made during the operation.
- Equipment inspection and maintenance log:
- Keep detailed records for all equipment used.
Working in confined spaces requires thorough preparation, proper training, and constant vigilance.
By following these requirements, risks can be significantly reduced, ensuring worker safety and the smooth execution of operations.